
Cathodic Protection: A Detailed Overview
Cathodic protection is a method used to prevent corrosion on metal surfaces. Corrosion is a natural process that occurs when metal comes into contact with water and oxygen. This process causes the metal to deteriorate and weaken over time, which can lead to structural failure and even safety hazards. Cathodic protection works by applying a direct current to the metal surface, which creates a protective oxide layer on the surface. This layer prevents further corrosion by blocking the flow of electrons from the metal to the surrounding environment. The direct current also helps to remove any existing corrosion on the surface.
Pros & Cons
One of the main advantages of cathodic protection is that it is a cost-effective way to prevent corrosion. It is also relatively easy to install and maintain. Cathodic protection can also be used in conjunction with other corrosion prevention methods to provide maximum protection. However, it is not suitable for all types of metal surfaces and can be less effective in certain environments. Additionally, cathodic protection may not be able to prevent corrosion in areas where the metal surface is damaged or has been exposed to harsh chemicals.
What Is Cathodic Protection Used For?
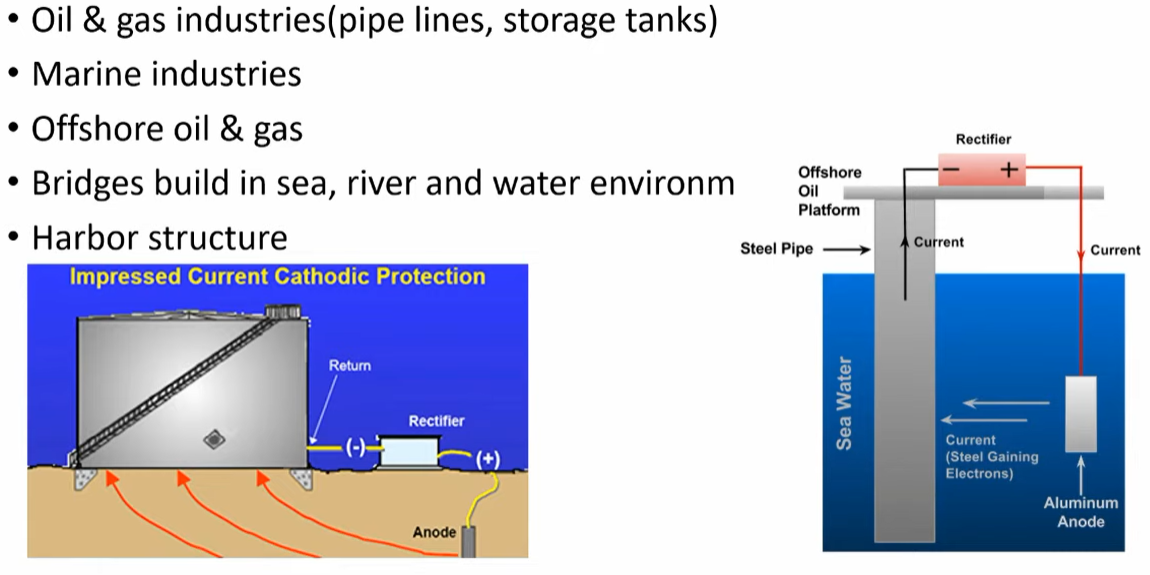
Cathodic protection is commonly used to protect metal structures such as pipelines, tanks, and ships. It is also used to protect underground metal structures such as buried pipelines and storage tanks. Cathodic protection is particularly useful for large metal structures that are difficult or impossible to replace, as well as for structures located in harsh environments where corrosion is a major concern.
How Does Cathodic Protection Work?
Cathodic protection works by applying a direct current to the metal surface. This direct current creates an electric field around the metal surface, which causes the metal to corrode at a slower rate. Additionally, the direct current also helps to remove any existing corrosion on the surface. The exact method of applying the direct current depends on the type of cathodic protection being used.
Types of Cathodic Protection
There are two basic types of cathodic protection:
- Galvanic cathodic protection
- Impressed current cathodic protection

Galvanic Cathodic Protection
Galvanic cathodic protection uses a galvanic anode, which is a metal that is more electrically active than the metal to be protected. When the anode is connected to the metal surface, it corrodes instead of the metal surface, which protects the metal from corrosion. The anode is connected to the metal surface through a conductive material such as copper wire. Galvanic cathodic protection is relatively simple and inexpensive, but it is not suitable for all types of metal surfaces and environments.
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection
Impressed current cathodic protection uses an external power source to apply a direct current to the metal surface. This type of cathodic protection is more versatile and can be used in a wider range of environments and on a wider range of metal surfaces. The power source is connected to the metal surface through a conductive material such as copper wire. Impressed current cathodic protection is more complex and expensive than galvanic cathodic protection, but it is more effective in certain environments and can be used on a wider range of metal surfaces. Additionally, impressed current cathodic protection can be adjusted to suit specific corrosion protection needs, which makes it a more flexible option. However, it requires regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure that it is functioning properly and providing adequate protection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cathodic protection is an effective method of preventing corrosion on metal surfaces. It is cost-effective and relatively easy to install and maintain. However, it is not suitable for all types of metal surfaces and environments. There are two basic types of cathodic protection: galvanic cathodic protection and impressed current cathodic protection. Galvanic cathodic protection is relatively simple and inexpensive, but impressed current cathodic protection is more versatile and can be adjusted to suit specific corrosion protection needs. It is important to consider the type of metal surface and environment when choosing a cathodic protection method.






0 Comments